Table 8 Trade specialization by category: Top 10 comparative advantages and disadvantages (contribution to the balance, in thousandths of the country's total trade, latest available year [t], evolution [t-10]-[t], and [t-10], evolution [1996]-[t-10])
Sources: CEPII, CHELEM – International Trade - Balance of Payments databases.
Notes:
Key points (comparative advantages) and weak points (comparative disadvantages) are calculated for the 72 categories of goods and for the 12 categories of services of CHELEM. Sometimes there are less than ten key points or ten weak points.
The changes over the period are calculated by subtraction and represent points of thousandths.
International specialization is measured by the contribution to the trade balance. For every country, this indicator calculates the revealed comparative advantages (RCA), ie the country's advantages/disadvantages revealed by international trade. Considering the country's exports and imports, it shows the key points and the weak points of the country, regardless of the impact of the macroeconomic situation of the country on its trade balance.
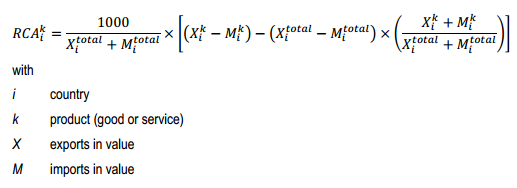
Trade balance of a product k is compared to a “theoretical balance” resulting from the distribution of the global balance observed between the various products in total trade of country i. This theoretical balance is, by construction, neutral towards any advantage or disadvantage of the country on the various products. So the distance between effective balance and theoretical balance on each of the products reveals the key or weak points of the country. The indicator is additive and the sum on all the products is equal to zero. To facilitate the comparisons between countries, the indicator is expressed in thousandths of the country's total trade.
Back





